Senegal Tax Rates
Senegal personal income tax is levied up to 50%.
Senegal Income tax is comprised of a progressive and a proportional tax. The rate of the proportional tax depends on the nature of the income:
wages and salaries: 11%
dividends: 10%
income from land: 20%
other income: 25%
In Senegal, taxable income is defined as income from all sources (wages and salaries, proceeds from agricultural, commercial or non commercial activities, income from real property, etc.). Each category of income is subject to a specific proportional duty taking into account different abatements and deductible charges and a progressive rate ranging from 0% to 50% based on the individual's family situation.
The progressive duty ranges from 0% to 50% and is applied per bracket of income, taking into account a dependents' allowance. The total income tax liability obtained by adding the proportional and progressive duties cannot exceed 50% of taxable income.
Basis - Residents are taxed on worldwide income, while nonresidents are taxed only on Senegal-source of income.
Residence - An individual is considered resident in Senegal for tax purposes if his/her permanent place of dwelling, centre of interests or centre of business is located in Senegal, or if he/she stays in Senegal for more than 183 days out of any 365-day period.
Tax Filing status - A taxpayer whose only source of income is salary, with tax withheld and paid by the employer, is exempt from the obligation to file a tax return. All other tax residents must file their own returns. Spouses are required to file separate tax returns.
Capital gains - Capital gains are taxable either at source by a notary in the case of a real estate transaction or based on the taxpayer's declaration.
Tax Deductions and tax allowances - Different abatements and allowable deductions apply to each category of income.
Other taxes on individuals:
Capital duty - No
Stamp duty - Stamp tax is levied on cash transactions based on the amount of the transaction.
Capital acquisitions tax - A 15% tax is levied on the value of real estate at the time of acquisition, and 1% on the value of securities and shares and other liquid assets.
Real estate tax - Property tax is due at a 5% or 7.5% rate.
Inheritance/estate tax - A 1% registration fee is imposed for deeds of pure and simple acceptance of succession or legacy. Inheritance tax is imposed at a 3% or 10% rate, depending on the degree of relationship.
Net wealth / net worth tax - No
Social security contributions - Social security is supported by the employer, with the annual ceiling for contributions set at XOF 756,000. The rate for family benefits is 7% and that for industrial accidents ranges from 1% to 5%, depending on the line of business.
National retirement fund contributions are paid by both the employer (60%) and the employee (40%). The rate of contributions for the general scheme is 14%, with an annual ceiling of XOF 3,072,000. The contribution rate for the executives' scheme is 6%, with an annual ceiling of XOF 9,216,000. Executive personnel must contribute to both schemes.
Senegal Tax year - Senegal tax year is the calendar year that ends on 31 December.
Tax Filing and tax payment - Tax returns must be filed by 31 January or 31 March of the following year depending on the type of income. Payment of tax must be made upon receipt of a tax notice.
Penalties - Penalties apply for late filing, late payment, failure to file and filing incorrect returns, with the amount depending on the nature of the tax and/or violation.
Senegal Corporate Tax Rate
The standard corporate tax rate in Senegal is 25%. Companies with "Free Exporting Enterprise" status are subject to a 15% tax rate.
Residence - An entity is generally deemed to be a resident of Senegal if its registered office, permanent establishment or centre of activity is located in Senegal.
Basis - Resident corporations are subject to tax on their worldwide income, while nonresidents are taxed only on Senegal source income.
Taxable income - Corporate income tax is imposed on net profits. Taxable profits are determined after deduction of allowable expenses and charges.
Taxation of dividends - Dividends received from a company, other than a subsidiary, are taxed as income after a 60% tax abatement on the gross amount of the dividends (see also under "Participation exemption").
Capital gains - Capital gains are treated as operating profits and included in the corporate income tax base.
Losses - Tax losses may be carried forward for 3 years. The carryback of losses is not permitted.
Surtax - No
Alternative minimum tax - A minimum tax is imposed, based on a company's turnover:
- XOF 500,000 for turnover up to XOF 250 million;
- XOF 750,000 for turnover between XOF 250 million and XOF 500 million;
- XOF 1 million for turnover over XOF 500 million.
Foreign tax credit - Senegal tax law does not provide for unilateral tax relief. A tax treaty, however, may provide for bilateral relief.
Participation exemption - An amount equal to 5% of dividends received by a resident parent company from its subsidiary is included in the taxable base (considered expenses incurred), unless the actual expenses incurred by the parent company are less than 5% of dividends received; in that case, only the actual amount is included in the taxable base.
Holding company regime - No
Tax Incentives - Tax incentives are granted under several laws, including the Investment Code, Mining Code, Petroleum Code, Environment Code, Free Zone Law, Free Exporting Companies Law, etc. Investments valued higher than XOF 250 billion are entitled to particular advantages negotiated directly between the investor and the ministry in charge, subject to non-objection from the Prime Minister.
Withholding tax:
Dividends - Dividends paid a nonresident company are subject to a 10% withholding tax, unless the rate is reduced under a tax treaty.
Interest - Interest paid to a company or individual is subject to a 16% withholding tax, unless the rate is reduced under a tax treaty. The tax rate is 8% for interest generated on a bank or stockbroker's account and 20% on interest on cash vouchers.
Royalties - Royalties paid to a foreign entity are subject to a 20% withholding tax, unless the rate is reduced under a tax treaty. Branch remittance tax - In certain cases, VAT (at 18%) can be applied on branch remittances.
Other taxes on corporations:
Capital duty - The initial capital duty is 1% of capital if the amount of capital is higher than XOF 10 million and XOF 25,000 in all other cases. The tax on a capital increase is 1% of the amount of the increase, with a 3% surtax in the case of contributions of real property.
Payroll tax - The payroll tax is 3% of taxable gross salary.
Real property tax - Tax is charged at 5% of the value of real property other than factories and industrial premises, and 7.5% of the value of factories and industrial premises.
Social security contributions - Social security is supported by the employer, with an annual ceiling for contributions of XOF 756,000. The rate for family benefits is 7% and that for industrial accidents ranges from 1% to 5%, depending on the line of business.
National retirement fund contributions are paid by both the employer (60%) and the employee (40%). The rate of contributions for the general scheme is 14%, with an annual ceiling of XOF 3,072,000. The contribution rate for the executives' scheme is 6%, with an annual ceiling of XOF 9,216,000. Executive personnel must contribute to both schemes.
Stamp duty - Stamp tax is levied on cash transactions based on the amount of the transaction.
Transfer tax - The tax rate depends on the nature of the transfer. For example, the rate on transfers of real property and goodwill is 15% and the rate on transfers of shares is 1%.
Other - A business license tax is comprised of a fixed annual payment and a proportional duty, with the amounts and rates fixed according to the nature and size of the business activity. Specific taxes are levied on the sale of petroleum products, alcohol and tobacco.
Anti-avoidance rules:
Transfer pricing - Payments for interest, royalties or any kind of services rendered by a resident company to another entity are deductible from the income tax base if the company can demonstrate that the payments are real, justified and the price was set under normal business conditions. The burden is on the company that made the payments to demonstrate that the payments meet these requirements.
Thin capitalisation - While Senegal does not have specific thin capitalisation rules, limits are imposed on interest paid to partners on funds provided by them to a company. The maximum interest rate is the lending rate of West African States Bank (BCEAO), plus 2 percentage points at the time the interest payment are due. Further, the loan may not exceed the amount of the share capital and the capital must be full paid in.
Controlled foreign companies - There are no specific CFC rules, but measures exist to prevent international tax evasion.
Administration and compliance:
Senegal Tax year - Senegal tax year is the calendar year that ends on 31 December.
Consolidated tax returns - Consolidation is necessary when a company established in Senegal controls other companies or exerts a notable influence on such companies.
Tax Filing requirements - A tax return must be filed by 30 April of the following year.
Penalties - Penalties apply for late filing, late payment, failure to file and filing an incorrect return. The amount of the penalty depends on the nature of the tax and/or violation.
Senegal vat (Value Added Tax)
Senegal has a single VAT rate of 18%.
Taxable transactions - All economic activities are within the scope of VAT, including activities of independent professionals. The main exemptions relate to health care, education, banking, insurance and reinsurance, farming and transportation. Banking transactions are subject to the tax on banking operations.
VAT Registration - All corporate businesses are required to register. Nonresident VAT payers are required to appoint a solvent resident representative to be jointly responsible for the payment of VAT and the discharge of other VAT-related obligations.
Filing and payment of VAT - Value Added Tax returns and payments are due on the 15th of the month following the date of the relevant transactions.
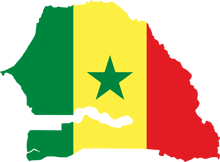
50%
25%
18%
Senegal
Income Tax Rate
Senegal
Corporate Tax Rate
Senegal
Sales Tax / VAT Rate
Last Update: Nov 2010
(This page may show previous year's tax rates. Always check last update time)
![]() ALBANIA
ALBANIA![]() ALGERIA
ALGERIA![]() ANDORRA
ANDORRA![]() ANGOLA
ANGOLA![]() ANGUILLA
ANGUILLA![]() ANTIGUA & BARBUDA
ANTIGUA & BARBUDA![]() ARGENTINA
ARGENTINA![]() ARUBA
ARUBA![]() AUSTRALIA
AUSTRALIA![]() AUSTRIA
AUSTRIA![]() AZERBAIJAN
AZERBAIJAN![]() BAHAMAS
BAHAMAS![]() BAHRAIN
BAHRAIN![]() BANGLADESH
BANGLADESH![]() BARBADOS
BARBADOS![]() BELARUS
BELARUS![]() BELGIUM
BELGIUM![]() BELIZE
BELIZE![]() BENIN
BENIN![]() BERMUDA
BERMUDA![]() BOSNIA & HERZEGOVINA
BOSNIA & HERZEGOVINA![]() BOTSWANA
BOTSWANA![]() BRAZIL
BRAZIL![]() BRITISH VIRGIN ISLANDS
BRITISH VIRGIN ISLANDS![]() BRUNEI
BRUNEI![]() BULGARIA
BULGARIA![]() BURKINA FASO
BURKINA FASO![]() BURMA
BURMA![]() BURUNDI
BURUNDI![]() CAMBODIA
CAMBODIA![]() CAMEROON
CAMEROON![]() CANADA
CANADA![]() CAPE VERDE
CAPE VERDE![]() CAYMAN ISLANDS
CAYMAN ISLANDS![]() CENTRAL AFRICAN REP.
CENTRAL AFRICAN REP.![]() CHAD
CHAD![]() CHILE
CHILE![]() CHINA
CHINA![]() COLOMBIA
COLOMBIA![]() COMOROS
COMOROS![]() CONGO, DEM. REPUBLIC
CONGO, DEM. REPUBLIC![]() CONGO, REPUBLIC OF
CONGO, REPUBLIC OF![]() COOK ISLANDS
COOK ISLANDS![]() COSTA RICA
COSTA RICA![]() COTE D'IVOIRE
COTE D'IVOIRE![]() CROATIA
CROATIA![]() CUBA
CUBA![]() CURAÇAO
CURAÇAO![]() CYPRUS
CYPRUS![]() CZECH REPUBLIC
CZECH REPUBLIC![]() DENMARK
DENMARK![]() DJIBOUTI
DJIBOUTI![]() DOMINICA
DOMINICA![]() DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
DOMINICAN REPUBLIC![]() ECUADOR
ECUADOR![]() EGYPT
EGYPT![]() EL SALVADOR
EL SALVADOR![]() EQUATORIAL GUINEA
EQUATORIAL GUINEA![]() ESTONIA
ESTONIA![]() FIJI
FIJI![]() FINLAND
FINLAND![]() FRANCE
FRANCE![]() FRENCH POLYNESIA
FRENCH POLYNESIA![]() GAMBIA
GAMBIA![]() GEORGIA
GEORGIA![]() GERMANY
GERMANY![]() GHANA
GHANA![]() GIBRALTAR
GIBRALTAR![]() GREECE
GREECE![]() GRENADA
GRENADA![]() GUATEMALA
GUATEMALA![]() GUERNSEY
GUERNSEY![]() GUYANA
GUYANA![]() HONDURAS
HONDURAS![]() HONG KONG
HONG KONG![]() HUNGARY
HUNGARY![]() ICELAND
ICELAND![]() INDIA
INDIA![]() INDONESIA
INDONESIA![]() IRAN
IRAN![]() IRELAND
IRELAND![]() ISLE OF MAN
ISLE OF MAN![]() ISRAEL
ISRAEL![]() ITALY
ITALY![]() IVORY COAST
IVORY COAST![]() JAMAICA
JAMAICA![]() JAPAN
JAPAN![]() JERSEY
JERSEY![]() JORDAN
JORDAN![]() KAZAKHSTAN
KAZAKHSTAN![]() KENYA
KENYA![]() KUWAIT
KUWAIT![]() LATVIA
LATVIA![]() LEBANON
LEBANON![]() LIBYA
LIBYA![]() LITHUANIA
LITHUANIA![]() LUXEMBOURG
LUXEMBOURG![]() MACAU
MACAU![]() MADAGASCAR
MADAGASCAR![]() MADEIRA
MADEIRA![]() MALAWI
MALAWI![]() MALAYSIA
MALAYSIA![]() MALDIVES
MALDIVES![]() MALTA
MALTA![]() MAURITIUS
MAURITIUS![]() MEXICO
MEXICO![]() MOLDOVA
MOLDOVA![]() MONACO
MONACO![]() MONTENEGRO
MONTENEGRO![]() MOROCCO
MOROCCO![]() MOZAMBIQUE
MOZAMBIQUE![]() MYANMAR
MYANMAR![]() NAMIBIA
NAMIBIA![]() NEPAL
NEPAL![]() NETHERLANDS
NETHERLANDS![]() NETHERLANDS ANTILLES
NETHERLANDS ANTILLES![]() NEW ZEALAND
NEW ZEALAND![]() NICARAGUA
NICARAGUA![]() NIGERIA
NIGERIA![]() NORWAY
NORWAY![]() OMAN
OMAN![]() PAKISTAN
PAKISTAN![]() PALESTINE
PALESTINE![]() PANAMA
PANAMA![]() PAPUA NEW GUINEA
PAPUA NEW GUINEA![]() PARAGUAY
PARAGUAY![]() PERU
PERU![]() PHILIPPINES
PHILIPPINES![]() POLAND
POLAND![]() PORTUGAL
PORTUGAL![]() PUERTO RICO
PUERTO RICO![]() QATAR
QATAR![]() ROMANIA
ROMANIA![]() RUSSIA
RUSSIA![]() RWANDA
RWANDA![]() SAUDI ARABIA
SAUDI ARABIA![]() SENEGAL
SENEGAL![]() SERBIA
SERBIA![]() SIERRA LEONE
SIERRA LEONE![]() SINGAPORE
SINGAPORE![]() SLOVAKIA
SLOVAKIA![]() SLOVENIA
SLOVENIA![]() SOUTH AFRICA
SOUTH AFRICA![]() SOUTH KOREA
SOUTH KOREA![]() SPAIN
SPAIN![]() SRI LANKA
SRI LANKA![]() SWAZILAND
SWAZILAND![]() SWEDEN
SWEDEN![]() SWITZERLAND
SWITZERLAND![]() SYRIA
SYRIA![]() TAIWAN
TAIWAN![]() TANZANIA
TANZANIA![]() THAILAND
THAILAND![]() TUNISIA
TUNISIA![]() TURKEY
TURKEY![]() TURKS AND CAICOS
TURKS AND CAICOS![]() UGANDA
UGANDA![]() UKRAINE
UKRAINE![]() UNITED ARAB EMIRATES
UNITED ARAB EMIRATES![]() UNITED KINGDOM
UNITED KINGDOM![]() UNITED STATES
UNITED STATES![]() URUGUAY
URUGUAY![]() UZBEKISTAN
UZBEKISTAN![]() VANUATU
VANUATU![]() VENEZUELA
VENEZUELA![]() VIETNAM
VIETNAM![]() WEST BANK
WEST BANK![]() YEMEN
YEMEN![]() ZAMBIA
ZAMBIA![]() ZIMBABWE
ZIMBABWE
© 2009-2012 TaxRates.cc
2011 - 2012 Tax Rate Guide and Tax Help Website