Malaysia Tax Rates
Malaysia individual income tax rates are progressive, up to 26%. Individuals who do not meet residence requirements are taxed at a flat rate of 26%.
Taxable Income RM Tax Rate Tax Payable RM
on the first 2,500 0% 0
on the next 2,500 1% 25
on the first 5,000 25
on the next 5,000 3% 150
on the first 10,000 175
on the next 10,000 3% 300
on the first 20,000 475
on the next 15,000 7% 1,050
on the first 35,000 1,525
on the next 15,000 12% 1,800
on the first 50,000 3,325
on the next 20,000 19% 3,800
on the first 70,000 7,125
on the next 30,000 24% 7,200
on the first 100,000 14,325
on the next 50,000 26% 13,000
on the first 150,000 27,325
on the next 100,000 26% 26,000
on 250,000 53,325
Above 250,000 26%
Basis - Individuals are taxed on income derived from Malaysia. Foreign-source income is not taxable in Malaysia.
Residence - An individual is considered tax resident if he/she is in Malaysia for 182 days or more in a calendar year. Alternatively, residence may be established by physical presence in Malaysia for a mere day if it can be linked to a period of residence of at least 182 consecutive days in an adjoining year.
Tax Filing status - A married couple living together may opt to file a joint or separate assessment.
Taxable income - Resident individuals are taxed at progressive rates ranging from 0% to 26%. Employment income includes most employment benefits whether in cash or in kind.
Capital gains - Capital gains are not taxed in Malaysia, except for gains derived from the disposal of real property or on the alienation of shares in a real property company. The real property gains tax, which applied to such gains, had been suspended since 1 April 2007, but is reinstated at a rate of 5% as from 1 January 2010.
Tax Deductions and tax allowances - Various allowances and personal deductions are available.
Other taxes on individuals:
Capital duty - No
Stamp duty - Stamp duty is levied at varying rates between 1% to 3% of the transacted value of property transfers and 0.3% on share transaction documents.
Capital acquisitions tax - No
Real property tax - Individual states in Malaysia levy "quit" rent and assessment at varying rates.
Inheritance/estate tax - No
Net wealth/net worth tax - No
Social security - Employees are required to make contributions to the EPF at a rate of 8% of remuneration and may contribute a nominal amount to the Social Security Organisation (SOCSO).
Administration and compliance:
Malaysia tax year - Malaysia tax year is the calendar year
Tax Filing and Tax payment - Tax on employment income is withheld by the employer under a pay as you earn (PAYE) scheme and remitted to the tax authorities. Malaysia imposes a self-assessment regime. An individual deriving employment income or business income must file a tax return and settle any balance owed by 30 April or 30 June respectively in the following calendar year.
Penalties - Penalties at various rates apply for failure to comply.
Malaysia Corporate Tax
The standard corporate tax rate in Malaysia is 25%, while resident small and medium-sized companies (i.e. companies capitalised at MYR 2.5 million or less and not part of a group having a company exceeding the above capitalisation threshold) are taxed at 20% on the first MYR 500,000, with the balance taxed at the 25% corporate tax rate:
- Company with paid up capital not more than RM2.5 million
. On first RM500,000 20%
. Subsequent Balance 25%
- Company with paid up capital more than RM2.5 million 25%
Residence - A corporation is resident in Malaysia if its management and control are exercised in Malaysia.
Basis - Corporations are taxed on income derived from Malaysia. Foreign-source income is not taxable unless the corporation is carrying on a business in the banking, insurance, air transport or shipping sectors.
Taxable income - Taxable income comprises all earnings derived from Malaysia, including gains or profits from a trade or business, dividends, interest, rents, royalties, premiums or other earnings.
Taxation of dividends - As from assessment year 2008, Malaysian companies are transitioning to the single tier system (STS) and phasing out the imputation system. Corporations in Malaysia have until 31 December 2013 to adopt the STS. Dividends received under the imputation system are taxable with a credit available for underlying corporate tax paid. Dividends paid by companies using the STS are not taxable.
Capital gains - Capital gains are not taxed in Malaysia, except for gains derived from the disposal of real property or on the alienation of shares in a real property company (RPC). The real property gains tax, which applied to such gains, had been suspended since 1 April 2007, but is reinstated at a rate of 5% as from 1 January 2010.
Losses - While losses can only be carried back for assessment years 2009 and 2010, they may be carried forward indefinitely (except where there is a substantial change in corporate ownership of a dormant company).
Surtax - No
Alternative minimum tax - A Labuan offshore company may elect to pay MYR 20,000 or to be taxed at 3% of the audited accounting profit.
Foreign tax credit - Foreign tax paid may be credited against Malaysian tax on the same profits (limited to 50% of foreign tax in the absence of a tax treaty), but the credit is limited to the amount of Malaysian tax payable on the foreign income.
Participation exemption - No, but foreignsource income is not taxable and local dividends do not attract further tax or are tax exempt.
Holding company regime - An investment holding company (IHC) is a company whose activities consist mainly of the holding of investments and that derives not less than 80% of its gross income, other than gross income from a source consisting of a business of holding of an investment, from such investments. Generally, only expenses falling within the definition of "permitted expenses" in the tax legislation would qualify for tax deduction in respect of an IHC.
Tax Incentives - A wide range of incentives are available for certain industries, such as manufacturing, IT services, biotechnology, Islamic finance, energy conservation and environment protection. Available incentives include: tax holidays of up to 10 years (pioneer status); investment tax allowances (i.e. 100% allowance on capital investments made up to 10 years); accelerated capital allowances; double deductions; and reinvestment allowances (i.e. 60% allowance on capital investments made in connection with approved projects).
Withholding tax:
Dividends - Malaysia does not levy withholding tax on dividends.
Interest - A withholding tax of 15% applies to interest paid to nonresidents, which may be reduced under an applicable tax treaty.
Royalties - A withholding tax of 10% applies to royalties paid to nonresidents, which may be reduced under an applicable tax treaty.
Other - A withholding tax of 10% applies to rentals of movable property, technical fees for services rendered in Malaysia and certain one-time income paid to nonresidents, which may be reduced under applicable tax treaties.
Branch remittance tax - No
Other taxes on corporations:
Capital duty - Capital duty is levied at rates ranging from MYR 1,000 to MYR 70,000.
Payroll tax - Tax on employment income is withheld by the employer under a pay as you earn (PAYE) scheme and remitted to the tax authorities.
Real property tax - Individual states in Malaysia levy "quit" rent and assessments at varying rates.
Social security - Employers and employees are required to make social security contributions to the Social Security Organisation (SOSCO). Generally, an employer contributes 1%-1.25% of an employee's remuneration. Employers and employees also must contribute to the Employees Provident Fund (EPF) at the rate of 12% and 8% of the employee's remuneration, respectively.
Stamp duty - Stamp duty is levied at varying rates between 1% to 3% of the transacted value of property transfers and 0.3% on share transaction documents.
Transfer tax - No, except for stamp duty.
Other - Equity requirements have been substantially relaxed as from 2009.
Anti-avoidance rules:
Transfer pricing - Transfer pricing rules are imminent and guidelines have been issued by the tax authorities. Taxpayers can request an advance pricing agreement.
Thin capitalisation - There are no specific thin cap rules, but legislation has been amended to allow for such rules.
Controlled foreign companies - No
Disclosure requirements - Yes
Administration and compliance:
Malaysia Tax year - Fiscal year (i.e. generally the accounting year).
Consolidated tax returns - Consolidation is not permitted as each company is required to file a separate tax return. However, subject to certain conditions, 70% of a company's adjusted loss may be used to set off profits of a related entity.
Tax Filing requirements - Malaysia imposes a self-assessment tax regime. Advance corporate tax is payable in 12 monthly instalments. A tax return must be filed within 7 months of the company's year end.
Penalties - Penalties at various rates apply for failure to comply.
Rulings - Taxpayers may request an advance ruling on the tax treatment of a specific transaction. Public rulings also are issued.
malaysia sales tax / service tax
Service tax and sales tax are currently the two major types of consumption taxes imposed on certain prescribed goods and services.
The rate of Sales Tax: 5%-10%
The rate of Service tax: 5%.
The Malaysian government has intended to widen the scope of indirect taxes by proposing to introduce Goods and Services Tax (GST). However, this move has been put on hold indefinitely.
SERVICE TAX
Service tax is a single stage tax applicable to certain prescribed goods and services in Malaysia. The tax also applies to professional and consultancy services as prescribed by the Malaysian customs authorities. The rate of service tax currently is fixed at 5% of the price, charge, or premium of the taxable goods or services prescribed.
Professional services provided by a company to companies within the same group will be exempted from service tax, subject to terms and conditions.
Generally, the imposition of service tax is subject to a specific threshold based on an annual turnover ranging from RM150,000 to RM500,000, subject to the types of taxable services and taxable person. The threshold would not apply for certain prescribed professional and consultancy services.
It is proposed that with effect from 1 January 2010, service tax be imposed on credit cards and charge cards including those issued free of charge as follows:
- RM50 per year on the principal card
- RM25 per year on the supplementary cards.
SALES TAX
Sales tax is a single stage tax imposed on taxable goods manufactured locally and/or imported. "Taxable goods" means goods of a class or kind not for the time being exempted from sales tax. Generally, all exports are exempted from sales tax.
Manufacturers of taxable goods are required to register with the custom authorities and to levy, charge and collect the tax from their customers. For imported goods, sales tax is collected from the importer upon the release of taxable goods from customs control.
Sales tax is an ad valorem and can be computed based on the value of taxable
goods sold, used, disposed of, or imported.
Sales tax is imposed on certain imported and locally manufactured goods under the Sales Tax Act 1972. The tax rate ranges from 5 - 10% for majority of the goods except for food preparations other than alcoholic and non-alcoholic compound preparations (other than those of heading No. 33.02) used for making beverages. Sales tax is also imposed on petroleum and petroleum products according to specific rates.
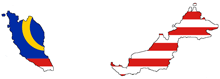
26%![]()
25%
5-10%
Malaysia
Income Tax Rate
Malaysia
Corporate Tax Rate
Malaysia
Sales Tax / VAT Rate
Last Update: Nov 2010
(This page may show previous year's tax rates. Always check last update time)
![]() ALBANIA
ALBANIA![]() ALGERIA
ALGERIA![]() ANDORRA
ANDORRA![]() ANGOLA
ANGOLA![]() ANGUILLA
ANGUILLA![]() ANTIGUA & BARBUDA
ANTIGUA & BARBUDA![]() ARGENTINA
ARGENTINA![]() ARUBA
ARUBA![]() AUSTRALIA
AUSTRALIA![]() AUSTRIA
AUSTRIA![]() AZERBAIJAN
AZERBAIJAN![]() BAHAMAS
BAHAMAS![]() BAHRAIN
BAHRAIN![]() BANGLADESH
BANGLADESH![]() BARBADOS
BARBADOS![]() BELARUS
BELARUS![]() BELGIUM
BELGIUM![]() BELIZE
BELIZE![]() BENIN
BENIN![]() BERMUDA
BERMUDA![]() BOSNIA & HERZEGOVINA
BOSNIA & HERZEGOVINA![]() BOTSWANA
BOTSWANA![]() BRAZIL
BRAZIL![]() BRITISH VIRGIN ISLANDS
BRITISH VIRGIN ISLANDS![]() BRUNEI
BRUNEI![]() BULGARIA
BULGARIA![]() BURKINA FASO
BURKINA FASO![]() BURMA
BURMA![]() BURUNDI
BURUNDI![]() CAMBODIA
CAMBODIA![]() CAMEROON
CAMEROON![]() CANADA
CANADA![]() CAPE VERDE
CAPE VERDE![]() CAYMAN ISLANDS
CAYMAN ISLANDS![]() CENTRAL AFRICAN REP.
CENTRAL AFRICAN REP.![]() CHAD
CHAD![]() CHILE
CHILE![]() CHINA
CHINA![]() COLOMBIA
COLOMBIA![]() COMOROS
COMOROS![]() CONGO, DEM. REPUBLIC
CONGO, DEM. REPUBLIC![]() CONGO, REPUBLIC OF
CONGO, REPUBLIC OF![]() COOK ISLANDS
COOK ISLANDS![]() COSTA RICA
COSTA RICA![]() COTE D'IVOIRE
COTE D'IVOIRE![]() CROATIA
CROATIA![]() CUBA
CUBA![]() CURAÇAO
CURAÇAO![]() CYPRUS
CYPRUS![]() CZECH REPUBLIC
CZECH REPUBLIC![]() DENMARK
DENMARK![]() DJIBOUTI
DJIBOUTI![]() DOMINICA
DOMINICA![]() DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
DOMINICAN REPUBLIC![]() ECUADOR
ECUADOR![]() EGYPT
EGYPT![]() EL SALVADOR
EL SALVADOR![]() EQUATORIAL GUINEA
EQUATORIAL GUINEA![]() ESTONIA
ESTONIA![]() FIJI
FIJI![]() FINLAND
FINLAND![]() FRANCE
FRANCE![]() FRENCH POLYNESIA
FRENCH POLYNESIA![]() GAMBIA
GAMBIA![]() GEORGIA
GEORGIA![]() GERMANY
GERMANY![]() GHANA
GHANA![]() GIBRALTAR
GIBRALTAR![]() GREECE
GREECE![]() GRENADA
GRENADA![]() GUATEMALA
GUATEMALA![]() GUERNSEY
GUERNSEY![]() GUYANA
GUYANA![]() HONDURAS
HONDURAS![]() HONG KONG
HONG KONG![]() HUNGARY
HUNGARY![]() ICELAND
ICELAND![]() INDIA
INDIA![]() INDONESIA
INDONESIA![]() IRAN
IRAN![]() IRELAND
IRELAND![]() ISLE OF MAN
ISLE OF MAN![]() ISRAEL
ISRAEL![]() ITALY
ITALY![]() IVORY COAST
IVORY COAST![]() JAMAICA
JAMAICA![]() JAPAN
JAPAN![]() JERSEY
JERSEY![]() JORDAN
JORDAN![]() KAZAKHSTAN
KAZAKHSTAN![]() KENYA
KENYA![]() KUWAIT
KUWAIT![]() LATVIA
LATVIA![]() LEBANON
LEBANON![]() LIBYA
LIBYA![]() LITHUANIA
LITHUANIA![]() LUXEMBOURG
LUXEMBOURG![]() MACAU
MACAU![]() MADAGASCAR
MADAGASCAR![]() MADEIRA
MADEIRA![]() MALAWI
MALAWI![]() MALAYSIA
MALAYSIA![]() MALDIVES
MALDIVES![]() MALTA
MALTA![]() MAURITIUS
MAURITIUS![]() MEXICO
MEXICO![]() MOLDOVA
MOLDOVA![]() MONACO
MONACO![]() MONTENEGRO
MONTENEGRO![]() MOROCCO
MOROCCO![]() MOZAMBIQUE
MOZAMBIQUE![]() MYANMAR
MYANMAR![]() NAMIBIA
NAMIBIA![]() NEPAL
NEPAL![]() NETHERLANDS
NETHERLANDS![]() NETHERLANDS ANTILLES
NETHERLANDS ANTILLES![]() NEW ZEALAND
NEW ZEALAND![]() NICARAGUA
NICARAGUA![]() NIGERIA
NIGERIA![]() NORWAY
NORWAY![]() OMAN
OMAN![]() PAKISTAN
PAKISTAN![]() PALESTINE
PALESTINE![]() PANAMA
PANAMA![]() PAPUA NEW GUINEA
PAPUA NEW GUINEA![]() PARAGUAY
PARAGUAY![]() PERU
PERU![]() PHILIPPINES
PHILIPPINES![]() POLAND
POLAND![]() PORTUGAL
PORTUGAL![]() PUERTO RICO
PUERTO RICO![]() QATAR
QATAR![]() ROMANIA
ROMANIA![]() RUSSIA
RUSSIA![]() RWANDA
RWANDA![]() SAUDI ARABIA
SAUDI ARABIA![]() SENEGAL
SENEGAL![]() SERBIA
SERBIA![]() SIERRA LEONE
SIERRA LEONE![]() SINGAPORE
SINGAPORE![]() SLOVAKIA
SLOVAKIA![]() SLOVENIA
SLOVENIA![]() SOUTH AFRICA
SOUTH AFRICA![]() SOUTH KOREA
SOUTH KOREA![]() SPAIN
SPAIN![]() SRI LANKA
SRI LANKA![]() SWAZILAND
SWAZILAND![]() SWEDEN
SWEDEN![]() SWITZERLAND
SWITZERLAND![]() SYRIA
SYRIA![]() TAIWAN
TAIWAN![]() TANZANIA
TANZANIA![]() THAILAND
THAILAND![]() TUNISIA
TUNISIA![]() TURKEY
TURKEY![]() TURKS AND CAICOS
TURKS AND CAICOS![]() UGANDA
UGANDA![]() UKRAINE
UKRAINE![]() UNITED ARAB EMIRATES
UNITED ARAB EMIRATES![]() UNITED KINGDOM
UNITED KINGDOM![]() UNITED STATES
UNITED STATES![]() URUGUAY
URUGUAY![]() UZBEKISTAN
UZBEKISTAN![]() VANUATU
VANUATU![]() VENEZUELA
VENEZUELA![]() VIETNAM
VIETNAM![]() WEST BANK
WEST BANK![]() YEMEN
YEMEN![]() ZAMBIA
ZAMBIA![]() ZIMBABWE
ZIMBABWE
© 2009-2012 TaxRates.cc
2011 - 2012 Tax Rate Guide and Tax Help Website